Introduction
This article elaborates the complete life cycle of making a custom interactive C# compiler much like one of the existing one CSC.exe. It is hard to imagine such custom C# interactive compiler kind of mechanism but this innovation could be constructed by employing C# APIs of the open source project, referred to as Mono. The development life cycle of this mechanism is relatively sophisticated and we can extend its features to be operable on Linux operating system also because Mono APIs are utilized here. Hence, we shall illustrate the development process in a comprehensive way, along with the live demonstration of this C# Interactive compiler.
Interactive Compiler
We have been primarily relying on Visual Studio IDE to compile C# programming code where csc.exe typically handles compilation related tasks. The .NET Framework stipulates range of compilers for various programming languages to debug an application and generate an executable. But such different-2 language compilation utilities interpret the whole application code file rather than a single code segment. This process is sometimes time consuming and creates unnecessary overhead on file system, even if in case of executing a very short code statement. We occasionally need to execute 1 or 2 lines of code for example, calculating Math function, LINQ statements. So, C# Interactive kind of mechanism is suitable which reflects immediate results, and spares the developer from hectic VS studio compilation process such as project creation and other configuration.
MONO especially has been sponsoring couple of interoperable projects which are not limited to a specific platform. It allows the developer to use their development API and evolved to build cross platform support application where Linux operating system and other wide range of platforms developer can also execute and run .NET application. The C# interactive compiler mechanism is constructed on top of the Mono.CSharp library by utilizing C# APIs. These APIs provides a C# compiler service that can be used to evaluate expressions and statements. Hence, the C# interactive shell allows dynamically evaluating C# programming code statements, as well as can be utilized for testing mini code fragments or writing scripts.
Essential
The C# interactive compiler code is typically developed by using C# language under .NET 4.0 Frameworks and classes which are responsible for providing custom compiler related functionality, are reference from Microsoft.CSharp.dll and Mono.ceil.dll.
Prototype
The C# Interactive Compiler operates through command line, typically provides DOS prompt like mechanism where we enters C# code statements, much like DOS commands entering, and it will reflect interpreted result. We don’t need to suffix semicolon in the code at command line, as per C# code semantics, just write the code statement and press enter.
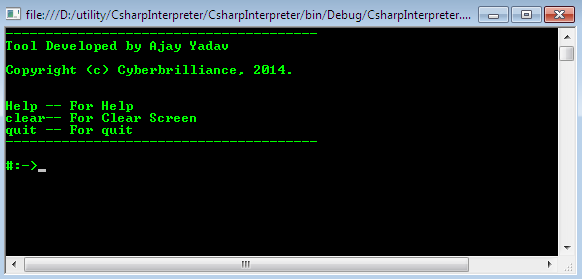
This command line utility, however, is able to compiler single line or multiline c# code. We shall demonstrate the working later in step by step format. Although such mechanism can build in GUI form also, this is relatively easy to operate rather than command line.
Getting Started
As we have noticed from the project prototypes, it would be a command line utility. Hence, create a Console based application as CsharpInterpreter.
Classes Blueprints
The C# Compiler design project is not limited to an entry class, rather its functionality is scattered in dozens of classes, some of them are static and abstracts. It is not possible to explain each class implementation in detail. Hence, we are presenting the employed classes through diagram blueprints, by which one can easily get an idea about the project inner working. Some classes are marked as abstracted in order to make their reference into other classes, which again inherited into another classes.


Entry Point
The making of this project is embarking from the Entry point Program class which is responsible from displaying command shell and other message. The backbone class of this project is Interactive class which contains the significant implementation about custom compilation process and obviously, called from entry point class.
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace CsharpInterpreter
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
if (args.Length > 0 && args[0].Equals
("--verbose", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase))
{
Interactive.Context.VerboseTrace = true;
}
Trace.Listeners.Add(new ConsoleTraceListener());
Program.WriteWelcomeMessage();
while (Interactive.Context.Continue)
{
Console.Write("#:->");
string text = Console.ReadLine();
if (text == null)
{
return;
}
try
{
string text2 = Interactive.Interpret(text);
if (text2 != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(text2);
}
}
catch (TargetInvocationException ex)
{
Program.WriteExceptionMessage(ex.InnerException);
}
catch (Exception ex2)
{
Program.WriteExceptionMessage(ex2);
}
}
}
private static void WriteWelcomeMessage()
{
Version version = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Version;
Console.WriteLine("---------------------------------------");
Console.WriteLine("Tool Developed by Ajay Yadav\n");
Console.WriteLine("Copyright (c) Cyberbrilliance, 2014.");
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("Help -- For Help");
Console.WriteLine("clear-- For Clear Screen");
Console.WriteLine("quit -- For quit");
Console.WriteLine("---------------------------------------");
Console.WriteLine();
}
private static void WriteExceptionMessage(Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Exception of type '" +
ex.GetType().Name + "' was thrown: " + ex.Message);
if (Interactive.Context.VerboseTrace)
{
Console.WriteLine("StackTrace:");
Console.WriteLine(ex.StackTrace);
if (ex.InnerException != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Inner Exception:");
Console.WriteLine(ex.InnerException.Message);
Console.WriteLine(ex.InnerException.StackTrace);
}
}
}
}
}
The program entry point class also handles any unexpected occurrence of error and maintaining a proper log database for each activity. Since the working of this utility is happening through command line and a separate session is required after executing the main project file, we shall enter C# code statements to compile them inline. Hence, it is mandatory to open a verbose mode through command line as:
if (args.Length > 0 && args[0].Equals
("--verbose", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase))
{
Interactive.Context.VerboseTrace = true;
}
Interpreter Class
The prime role of this class is to avail C# custom provider from CodeDom class and invoke the entered C# inline or multiline programming statements. This class is basically a custom grammar for this project which checks what kind of statements are entered by user such as using, expression and generic statements.
public static class Interactive
{
private static readonly CodeDomProvider Compiler;
public static exeContext Context;
static Interactive()
{
Interactive.Compiler = CodeDomProvider.CreateProvider("C#");
Interactive.Context = new exeContext();
}
public static void Reset()
{
Interactive.Context = new exeContext();
}
public static string Interpret(string sourceCode)
{
return sourceCode.CompileCodeSnippet().Invoke();
}
private static compiledCode CompileCodeSnippet(this string code)
{
if (Interactive.Context.MultiLine)
{
exeContext expr_11 = Interactive.Context;
expr_11.MultiLineStatement += code;
code = Interactive.Context.MultiLineStatement;
}
return code.Statement() || code.TypeMember();
}
private static compiledCode Statement(this string code)
{
return code.ExpressionStatement() ||
code.UsingStatement() || code.GenericStatement();
}
private static compiledCode UsingStatement(this string code)
{
compiledCode result = null;
if (code.TrimStart(new char[0]).StartsWith("using "))
{
string text = code.TrimEnd(new char[0]);
if (!text.EndsWith(";"))
{
text += ";";
}
string usingStatement = text;
string source = Interactive.Program(null, null, null, null, usingStatement);
custStatement statement = new custStatement(code, source.CompileFromSource());
if (!statement.HasErrors)
{
Interactive.Context.UsingStatements.Add(text);
result = statement;
}
}
return result;
}
private static compiledCode GenericStatement(this string code)
{
compiledCode result = null;
string statement = code + ";";
string source = Interactive.Program(null, statement, null, null, null);
custStatement statement2 = new custStatement(code, source.CompileFromSource());
if (!statement2.HasErrors)
{
Interactive.Context.CallStack.Add(code + ";");
result = statement2;
}
else
{
if (!Interactive.Context.MultiLine &&
(statement2.Errors[0].ErrorNumber == "CS1513"
|| statement2.Errors[0].ErrorNumber == "CS1528"))
{
Interactive.Context.MultiLine = true;
exeContext expr_A2 = Interactive.Context;
expr_A2.MultiLineStatement += code;
}
}
return result;
}
private static compiledCode ExpressionStatement(this string expr)
{
string returnStatement = custProBuilds.ReturnStatement(expr);
custExpression expression = new custExpression
(expr, Interactive.Program
(null, null, returnStatement, null, null).CompileFromSource());
if (!expression.HasErrors &&
!expr.Trim().Equals("clear", StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
string text = "__" +
Guid.NewGuid().ToString().Replace("-", "");
Interactive.Context.CallStack.Add(string.Concat(new string[]
{
"var ",
text,
" = ",
expr,
";"
}));
}
return expression;
}
public static string Program(string typeDeclaration = null,
string statement = null, string returnStatement = null,
string memberDeclaration = null, string usingStatement = null)
{
return custProBuilds.Build(Interactive.Context, typeDeclaration,
statement, returnStatement, memberDeclaration, usingStatement);
}
private static compiledCode TypeMember(this string source)
{
return source.TypeDeclaration() ||
source.MemberDeclaration() || source.FieldDeclaration();
}
private static compiledCode MemberDeclaration(this string code)
{
custMemDecl memberDeclaration = new custMemDecl(code,
Interactive.Program(null, null, null, code, null).CompileFromSource());
if (!memberDeclaration.HasErrors)
{
Interactive.Context.MemberDeclarations.Add(code);
}
return memberDeclaration;
}
private static compiledCode TypeDeclaration(this string source)
{
string source2 = Interactive.Program(source, null, null, null, null);
custTypeDecl typeDeclaration =
new custTypeDecl(source, source2.CompileFromSource());
if (!typeDeclaration.HasErrors)
{
Interactive.Context.TypeDeclarations.Add(source);
}
return typeDeclaration;
}
private static compiledCode FieldDeclaration(this string code)
{
string text = code + ";";
string memberDeclaration = text;
custMemDecl memberDeclaration2 = new custMemDecl(code,
Interactive.Program
(null, null, null, memberDeclaration, null).CompileFromSource());
if (!memberDeclaration2.HasErrors)
{
Interactive.Context.MemberDeclarations.Add(text);
}
return memberDeclaration2;
}
private static string Invoke(this compiledCode compiledCode)
{
if (Interactive.Context.MultiLine && !compiledCode.HasErrors)
{
Interactive.Context.MultiLine = false;
Interactive.Context.MultiLineStatement = "";
}
if (!Interactive.Context.MultiLine && compiledCode.HasErrors)
{
Interactive.TraceErrorMessage(compiledCode);
}
if (!Interactive.Context.MultiLine && !compiledCode.HasErrors &&
(compiledCode is custExpression || compiledCode is custStatement))
{
Interactive.Context.MultiLine = false;
Interactive.Context.MultiLineStatement = "";
object result = Interactive.InvokeCompiledResult(compiledCode.Results);
if (compiledCode is custExpression)
{
return result.FormatOutput();
}
}
return null;
}
private static void TraceErrorMessage(compiledCode compiledCode)
{
Trace.TraceError(compiledCode.Errors[0].ErrorText);
if (Interactive.Context.VerboseTrace)
{
Trace.TraceError(compiledCode.Errors[0].ErrorNumber);
}
}
private static object InvokeCompiledResult(CompilerResults results)
{
Assembly compiledAssembly = results.CompiledAssembly;
Type type = compiledAssembly.GetType("Wrapper");
object obj = Activator.CreateInstance(type, null);
MethodInfo method = type.GetMethod("Eval");
return method.Invoke(obj, null);
}
private static CompilerResults CompileFromSource(this string source)
{
CompilerParameters compilerParameters = new CompilerParameters
{
GenerateExecutable = false,
GenerateInMemory = true
};
compilerParameters.ReferencedAssemblies.Add("System.Core.dll");
compilerParameters.ReferencedAssemblies.Add
(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().Location);
compilerParameters.ReferencedAssemblies.Add("System.Xml.dll");
compilerParameters.ReferencedAssemblies.Add("System.Xml.Linq.dll");
compilerParameters.ReferencedAssemblies.Add("System.Windows.Forms.dll");
foreach (string current in exeContext.Assemblies)
{
compilerParameters.ReferencedAssemblies.Add(current);
}
return Interactive.Compiler.CompileAssemblyFromSource(compilerParameters, new string[]
{
source
});
}
}
The implementation for each semantic is resided in separated methods which reference is passed to build method later. As we know, each C# code definition is located into external DLL files which are typically imported into code file through using statements. Some of the namespaces are automatically imported to class file. Hence, this project also provides the definition for some default namespace in CompilerFromSource() method. It doesn’t mean that whatever we enter on the command line shell is interpreted perfectly. This mechanism also echoes error message, in case of not recognizing code grammar.
Loading Context Class
The Context class is used to load the external or default namespace (DLL) in the C# Interactive interface so that user is spared from importing, even some common namespaces frequently. It also gathers the information about the verbose mode, Single/Multiline statements, using statements and later, reference in the CompilerFromSource() method of the Interpreted class.
public class exeContext
{
public static List<string> Assemblies = new List<string>();
public IList<string> CallStack = new List<string>();
public IList<string> TypeDeclarations = new List<string>();
public List<string> MemberDeclarations = new List<string>();
public List<string> UsingStatements = new List<string>();
public bool MultiLine
{
get;
set;
}
public string MultiLineStatement
{
get;
set;
}
public bool VerboseTrace
{
get;
set;
}
public bool Continue
{
get;
set;
}
public exeContext()
{
this.Continue = true;
this.MultiLineStatement = "";
}
public static void LoadAssembly(string name)
{
FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo(name);
FileInfo fileInfo2 = new FileInfo(Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().Location);
if (fileInfo.DirectoryName != fileInfo2.DirectoryName)
{
if (fileInfo2.DirectoryName != null)
{
if (!File.Exists(Path.Combine
(fileInfo2.DirectoryName, fileInfo.Name)))
{
fileInfo.CopyTo(Path.Combine
(fileInfo2.DirectoryName, fileInfo.Name), true);
}
exeContext.Assemblies.Add(fileInfo.Name);
return;
}
}
else
{
exeContext.Assemblies.Add(name);
}
}
}
Custom Build Class
The custProBuilds class mainly has to two methods as Build() and ReturnStatment(). These methods usually generate code dynamically, and are called from Interactive class. C# code typically requires semicolon as a terminated statement, but here we can either place or not, because such handling is care by ReturnStatement() method automatically. The run time C# code is entered on command shell gathered from the Interactive class and pass to Build() to generated code, which is later compiled.
public static class custProBuilds
{
public const string UsingStatements =
"\r\nusing System;\r\nusing System.Collections.Generic;\r\nusing System.Text;
\r\nusing System.Linq;\r\nusing System.Xml;\r\nusing System.Xml.Linq;
\r\nusing CsharpInterpreter;\r\nSystem.Windows.Forms;\r\n";
private const string ClassPrefix = "public class Wrapper { \r\n";
private const string InteropDeclarations =
"public void LoadAssembly(string name) \r\n
{ \r\nexeContext.LoadAssembly(name);
\r\n }\r\n\r\n public bool Verbose \r\n {\r\nget
{ return Interactive.Context.VerboseTrace;
}\r\n set { Interactive.Context.VerboseTrace = value; }\r\n }\r\n\r\npublic OutputString Exit
\r\n {\r\n get { Interactive.Context.Continue = false;
return new OutputString(\"Bye\");
}\r\n }\r\n public OutputString exit \r\n {\r\n get { return Exit; }\r\n }\r\n\r\n
public OutputString Quit \r\n {\r\n get { return Exit; }\r\n }\r\n\r\n
public OutputString quit \r\n {\r\n get { return Exit; }\r\n }\r\n\r\n\r\n
ublic OutputString Help \r\n {\r\n get
{ return new OutputString(@\"Usings\t\t\tDisplay the current using statements\n
Help\t\t\tDisplay help\n Clear\t\t\tClear the console window\n
Quit\t\t\tExit\"); }\r\n }
\r\n\r\n public OutputString __Program \r\n {\r\n get
{ return new OutputString(Interactive.Program()); }\r\n }\r\n\r\n
public OutputString Usings \r\n {\r\n get
{ return new OutputString(custProBuilds.UsingStatements); }\r\n }\r\n\r\n
public outString Clear \r\n {\r\n get { Console.Clear();
return new outString(\"\"); }\r\n }\r\n\r\n public outString clear \r\n
{\r\n get { return Clear; }\r\n }\r\n\r\n";
private const string FuncPrefix = " public object Eval() { \r\n";
private const string ReturnStmnt = " return ";
private const string FuncSuffix = " \r\n }\r\n}";
private static exeContext context;
private static readonly string DefaultReturnStatement =
custProBuilds.ReturnStatement("\"\"");
public static string ReturnStatement(string expression)
{
return " return " + expression + ";";
}
public static string Build(exeContext executionContext, string typeDeclaration,
string statement, string returnStatement, string memberDeclaration, string usingStatement)
{
custProBuilds.context = executionContext;
return string.Concat(new string[]
{
"\r\nusing System;\r\nusing System.Collections.Generic;
\r\nusing System.Text;
\r\nusing System.Linq;\r\nusing System.Xml;
\r\nusing System.Xml.Linq;\r\nusing CsharpInterpreter;\r\n",
custProBuilds.CustomUsingStatements(),
usingStatement,
custProBuilds.TypeDeclarations(),
typeDeclaration,
"public class Wrapper { \r\n",
custProBuilds.MemberDeclarations(),
memberDeclaration,
" public void LoadAssembly(string name)
\r\n { \r\nexeContext.LoadAssembly(name);
\r\n }\r\n\r\n public bool Verbose \r\n {\r\n
get { return Interactive.Context.VerboseTrace; }\r\n
set { Interactive.Context.VerboseTrace = value; }\r\n }\r\n\r\n
public outString Exit \r\n {\r\n
get { Interactive.Context.Continue = false;
return new outString(\"Bye\"); }\r\n }\r\n
public outString exit \r\n {\r\n
get { return Exit; }\r\n }\r\n\r\n
public outString Quit \r\n {\r\n
get { return Exit; }\r\n }\r\n\r\n
public outString quit \r\n {\r\n
get { return Exit; }\r\n }\r\n\r\n\r\n
public outString Help \r\n {\r\n
get { return new outString(@\"\n
Usings\t\t\tDisplay the current using statements\n
Help\t\t\tDisplay help\n Clear\t\t\tClear the console window\n
Quit\t\t\tExit\"); }\r\n }\r\n\r\n public outString __Program \r\n
{\r\n get { return new outString(Interactive.Program());
}\r\n }\r\n\r\n
public outString Usings \r\n {\r\n
get { return new outString(custProBuilds.UsingStatements);
}\r\n }\r\n\r\n public outString Clear \r\n {\r\n
get { Console.Clear(); return new outString(\"\"); }\r\n
}\r\n\r\n public outString clear \r\n {\r\n
get { return Clear; }\r\n }\r\n\r\n public object Eval() { \r\n",
custProBuilds.CallStack(),
statement,
returnStatement ?? custProBuilds.DefaultReturnStatement,
" \r\n }\r\n}"
});
}
private static string CallStack()
{
return custProBuilds.CreateInlineSectionFrom(custProBuilds.context.CallStack);
}
private static string MemberDeclarations()
{
return custProBuilds.CreateInlineSectionFrom(custProBuilds.context.MemberDeclarations);
}
private static string TypeDeclarations()
{
return custProBuilds.CreateSectionFrom(custProBuilds.context.TypeDeclarations);
}
private static string CustomUsingStatements()
{
return custProBuilds.CreateSectionFrom(custProBuilds.context.UsingStatements);
}
private static string CreateInlineSectionFrom(IEnumerable<string> linesOfCode)
{
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
foreach (string current in linesOfCode)
{
stringBuilder.Append(" ");
stringBuilder.Append(current);
stringBuilder.Append("\r\n");
}
return stringBuilder.ToString();
}
private static string CreateSectionFrom(IEnumerable<string> linesOfCode)
{
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
foreach (string current in linesOfCode)
{
stringBuilder.Append(current);
stringBuilder.Append("\r\n");
}
return stringBuilder.ToString();
}
}
Custom Output Class
The result of the dynamic code which is entered on the Interactive command shell is compiled and its result is taken care by custOutput class. First, this class recognizes the entire output, which is stored in XML format, Array and later retrieved on the interactive shell through enumerator. All the formatted output handling is done by StringBuilder class here.
public static class custOutput
{
public static string FormatOutput(this object result)
{
if (result == null)
{
return "null";
}
if (result is string)
{
return custOutput.FormatOutput(result as string);
}
if (result is short || result is int || result is long || result is double ||
result is float || result is bool || result.GetType().Name.Contains("AnonymousType"))
{
return result.ToString();
}
if (result is IDictionary)
{
return custOutput.FormatOutput(result as IDictionary);
}
if (result is Array)
{
return custOutput.FormatOutput(result as Array);
}
if (result is IXPathNavigable)
{
IXPathNavigable iXPathNavigable = result as IXPathNavigable;
XPathNavigator xPathNavigator = iXPathNavigable.CreateNavigator();
return XDocument.Parse(xPathNavigator.OuterXml).ToString();
}
if (result is XDocument)
{
return result.ToString();
}
if (result is IEnumerable)
{
return custOutput.FormatOutput(result as IEnumerable);
}
MethodInfo method = result.GetType().GetMethod("ToString", Type.EmptyTypes);
if (method != null && method.DeclaringType != typeof(object))
{
return result.ToString();
}
if (result.GetType() != typeof(object))
{
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
Type type = result.GetType();
stringBuilder.Append(type.Name);
stringBuilder.Append(" {");
int num = 0;
PropertyInfo[] properties = type.GetProperties();
for (int i = 0; i < properties.Length; i++)
{
PropertyInfo propertyInfo = properties[i];
if (propertyInfo.MemberType == MemberTypes.Property)
{
stringBuilder.Append(" ");
stringBuilder.Append(propertyInfo.Name);
stringBuilder.Append(" = ");
stringBuilder.Append(propertyInfo.GetValue(result, null).FormatOutput());
if (num < type.GetProperties().Length - 1)
{
stringBuilder.Append(", ");
}
}
num++;
}
stringBuilder.Append(" }");
return stringBuilder.ToString();
}
return result.ToString();
}
private static string FormatOutput(Array array)
{
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("[");
int num = 0;
foreach (object current in array)
{
stringBuilder.Append(current.FormatOutput());
if (num < array.Length - 1)
{
stringBuilder.Append(",");
}
num++;
}
stringBuilder.Append("]");
return stringBuilder.ToString();
}
private static string FormatOutput(string value)
{
return "\"" + value + "\"";
}
private static string FormatOutput(IEnumerable enumerable)
{
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("[");
IEnumerator enumerator = enumerable.GetEnumerator();
int num = 0;
while (enumerator.MoveNext())
{
stringBuilder.Append(enumerator.Current.FormatOutput());
stringBuilder.Append(",");
num++;
}
if (num > 0)
{
stringBuilder.Remove(stringBuilder.Length - 1, 1);
}
stringBuilder.Append("]");
return stringBuilder.ToString();
}
private static string FormatOutput(IDictionary dictionary)
{
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("[");
IDictionaryEnumerator enumerator = dictionary.GetEnumerator();
int num = 0;
while (enumerator.MoveNext())
{
stringBuilder.Append("[");
stringBuilder.Append(enumerator.Key.FormatOutput());
stringBuilder.Append(", ");
stringBuilder.Append(enumerator.Value.FormatOutput());
stringBuilder.Append("]");
stringBuilder.Append(",");
num++;
}
if (num > 0)
{
stringBuilder.Remove(stringBuilder.Length - 1, 1);
}
stringBuilder.Append("]");
return stringBuilder.ToString();
}
}
So, we have explained the main-2 coding segments up till now, rest of the classes implementation in this scenario is subtle and their code is could be found in the attachment. We can’t discuss each here, due to the length of this paper. Once all the classes’ code is write properly and when we test it, the Interactive compiler IDE shown as follows:

In the aforesaid figure, we can see an overview of results of short C# code. We don’t need to create a separate project, even to compile short codes. If we want to see the command help of this software, then issue Help command, for quitting the application issue quit command and for clearing the command window test, issue clear command as follows:

Suppose we would like to do some window form related operation, like appearing a message box, then first use the namespace of Windows forms and issue this code on the interactive shell pertaining to message box shown as follows:

Final Words
This article has given a taste of programming in a functional language, a dynamic language like Perl, Python or BASIC. It is hard to find C# interactive kind of mechanism so far, but this dream comes true by employing Mono project API. In this paper, I have illustrated the comprehensive development process of C# interactive programming where we can enter the C# code at run time and get the results immediately, even without making or relying on a full-fledged VS project. We shall present other .NET DLR projects likes IronPython and IronRuby in the form of Interactive shell soon.
Ajay Yadav is an author, Cyber Security Specialist, Subject-Matter-Expert, Software Engineer, and System Programmer with more than eight years of work experience on diverse technology domains. He earned a Master and Bachelor Degree in Computer Science, along with numerous premier professional certifications from Microsoft, EC-council, and Red-hat. For several years, he has been researching on Reverse Engineering, Secure Source Coding, Advance Software Debugging, Vulnerability Assessment, System Programming and Exploit Development. He is a regular contributor to various international programming journals as well as assists developer community with writing blogs, research articles, tutorials, training material and books on sophisticated technology. His spare time activity includes tourism, movies and meditation. He can be reached at om.ajay007@gmail.com;
 General
General  News
News  Suggestion
Suggestion  Question
Question  Bug
Bug  Answer
Answer  Joke
Joke  Praise
Praise  Rant
Rant  Admin
Admin