The Intel® Core™ M Processor
5.00/5 (1 vote)
This article, aimed at developers, will provide a glimpse into this 64-bit, multi-core SOC processor, and gives an overview of the available Intel® technologies, including Intel® HD Graphics 5300.
Abstract
Intel is introducing the first of the 5th generation processors (code named Broadwell) with the launch of three SKUs in the Intel® Core™ M Processor family. This article, aimed at developers, will provide a glimpse into this 64-bit, multi-core SOC processor, and gives an overview of the available Intel® technologies, including Intel® HD Graphics 5300.
Key Intel Core M Processor Features
The Intel® Core™ M Processor family provides better performance in a smaller package requiring less power and cooling (great for thin, fanless designs) with longer battery life and includes:
- Intel HD5300 Graphics & Intel® Wireless Display 5.0
- Intel Wireless-AC 7265 & (2015) Wireless Docking support with WiGig
- Intel® Smart Sound Technology
- Intel® Platform Protection Technology and other security features
Size Reduction + Performance Improvements = Reduction in Power & Cooling Requirements
The Intel Core M processor is the first to be released on 14nm technology. The die size has been reduced by over 30%, even though the number of transistors has increased by over 300 million. The Intel Core M processor also features a lower power footprint, which produces less heat. The three SKUs being released in the 4th quarter of 2014 are built to run with only 4.5 watts, which means they can run without a fan! These SKUs provide great performance especially on ultra-thin (less than 9mm) form factors including tablets and 2 in 1s.
|
Figure 1: Small Low Power Intel Core M Processor Comparisons
|
The graph on the left side of Figure 1 shows the thermal design power drop from 18W in 2010 to 4.5W with the Intel Core M processor. That’s a 4X reduction over 4 years and a 60% reduction from 2013 On the right side of Figure 1, the size comparison shows the dimensions of the 4th generation Intel® Core™ processor compared to the new Intel Core M processor. And in reducing the package footprint by ~50%, Intel achieved a ~25% reduction in board area. |
| Smaller in all dimensions than the 4th generation Intel Core processor, the Intel Core M processor provides dual CPU cores with a 4MB cache. With Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology, four threads can run simultaneously. With Intel® TurboBoost Technology 2.0, the 0.8 GHz core frequency processors can reach 2.0 GHz, while the 1.1 core frequency, the Intel Core M processor 5Y70 can reach 2.6 GHz. | 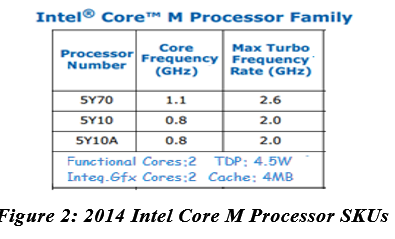 |
Given the 1.3 billion transistors providing the CPU, Graphics, Memory Controller, Audio, and connectivity in one package, there won’t be any loss in performance. In fact comparison tests with the previous generation Intel® Core™ processor i5-4320Y, showed significant performance improvements (see Figure 3).

Power Technology
|
Throughout this document you will see many Intel technologies used to keep power draw at a minimum.
|
 |
Other components all have improved power management features that are covered in their respective sections below.
The Rest of the Package
The Intel Core M package shares a die with a low power PCH with intelligent power throttling that supports PCIe NAND, PCIe 2.0 (12 lanes at x1,x2,or x4) and adds 2 additional USB 2.0 ports.
The Integrated Memory Controller supports Intel® Fast Memory Access and Intel® Flex-Memory Access and saves power using conditional self-refresh, dynamic power-down and disabling unused system memory via 4 power down modes while supporting DDR3L or LPDDR3 RAM at 1600 or 1333 split into 2 channels.
Intel® HD Graphics 5300
As the new addition to the Intel HD Graphics family, Intel HD Graphics 5300 starts at a 100MHz base that has a max dynamic frequency of 800MHZ (850MHz on the 5Y70). With Intel® Quick Sync Video (encode and post processing for media and visual intensive apps), Intel® InTru™ 3D Technology, Intel® Clear Video HD Technology, and Intel® Flexible Display Interface (Intel® FDI ),the Intel HD Graphics 5300 supports 3 displays (eDP/DP/HDMI). Using the family’s GT2 processor (with 189 million transistors), HD Graphics 5300 has 24 shading units, 4 TMUs, and 1 ROP with support for DirectX* 11.1+, OpenGL* 4.2, OpenCLTM 2.0, Shader Model 5.0 while providing up to UltraHD resolution (3840x2160) via HDMI @ 24Hz.

Testing has shown converting HD video using Cyberlink* MediaEsspresso* ran at up to 80% faster than the prior generation Core i5 processor, and that games (3DMark* IceStorm Unlimited v 1.2.) ran up to 40% better. Yet the Intel Core M processors still provided an extra 1.7 hours of battery life (based on local video playback and 35WHr battery).
(All tests conducted on Intel Reference Platforms with 4 GB Dual Channel LPDDR3-1600 (2x2GB) with Intel 160GB SSD running Windows 8.1 Update RTM. Core M used BIOS v80.1 while Core i5-4302Y (previous gen) w used BIOS WTM137. Both gen used Intel® HD Graphics driver v. 15.36.3650 and had TDP of 4.5W. Other settings: System Power Management Policy: Balanced, Wireless: On and connected, Battery size assumption: 35WHr.)
The extra battery life is possible since Intel HD Graphics 5300 has:
- Intel® Display Power Savings Technology (Intel DPST) 6.0, which reduces backlighting while increasing contrast ad brightness.
- Intel® Automatic Display Brightness, which uses a front panel sensor to adjust to ambient light
- Intel® Seamless Display Refresh Rate Technology (SDRRS Technology), which lowers the refresh rate when running off the battery.
- Intel® Rapid Memory Power Management (Intel® RMPM), which allows automatic memory refresh from low power states
- Graphics Render C-state (RC6), which changes the power rail to low voltage when there is no workload.
- Intel® Smart 2D Display Technology (Intel® S2DDT), which reduces memory reads for display refresh (only available in single pipe mode and not for use with 3D applications)
- Intel® Graphics Dynamic Frequency Technology, which opportunistically increases frequency and voltage based on performance needs
2nd gen Intel® Wireless-AC7265 cards
| The Intel Core M processor family also introduces faster WLAN (performance improves 15-100%) while having a 70% smaller footprint by using the M.2 1216 form factor. |  |
Compared to the dual-band Intel® Wireless-A7260, the AC7265 has improved link reliability, broader coverage, support for more devices and can stream video at 1080p while being 50% greener at idle (4mW) and 30% greener when active (8mW during web browsing).
Note: Intel plans to introduce wireless docking with WiGig into the Intel Core M family in 2015.
Intel® Wireless Display 5
This new generation of Intel® Wireless Display (aka Intel® WiDi) supports a resolution of 1920x1080p@60fps, as well as reduced connection time (under 6 seconds) and reduced gaming latency (under 65ms).
Technologies include:
- HDCP 2.2
- Adaptive scaling and frame rate
- UoIP for multi-point touch screen or gesture control
- Intel® Update Manager integrated to simplify driver update
- Support of all DX9/DX11 full screen game formats with gaming mode detect
- Intel WiDi Remote bundled for multi-window management on dual screens
- Additional features in Intel Pro WiDi, aimed at conference room usage:
- DCM (different channel mode),
- Privacy screen,
- WPAN isolation
- Manageability
See also Building Intel® WiDi Apps for UltrabookTM
Intel® Smart Sound Technology
With a new, more powerful integrated DSP I2S in the PCH, Intel Smart Sound Technology (Intel® SST) reduces platform power by offloading audio processing from the host CPU with support for decoding of MP3/AAC, Waves* or DTS* post processing, and wake on voice. The I2S codec must be used for Intel SST.
Security including Intel® Platform Protection Technology
Systems with Intel Core M processors come with enhanced security features including:
- Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT-d and Intel® VT-x with EPT ) - optimizes VM memory use and allows QoS guarantees
- Intel® Advanced Encryption Standards -New Instructions (Intel® AES-NI) - 6 Intel® SSE instructions for high performance security
- Intel® Secure Key - dynamic random number generator
- PCLMULQDQ (carry-less multiplication) - often used in cryptography
- OS Guard
- Execute Disable (ND) Bit
- SMEP (Supervisor Mode Execution Protection) and SMAP (Supervisor Mode Access Protection)
- Intel® Device Protection with Boot Guard
- Intel® Active Management Technology v10
Note: The Intel Core M processor 5Y70 additionally supports Intel vPro™ Technology and Intel® Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT) and Windows* Instant Go* (aka Connected Standby).
Developer Recommendations
Consider the following features and calls when developing applications for the Intel Core M processor family.
- With Intel SpeedStep technology, use the MWAIT instruction and substates for most power state transitions; but for C1/C1E states, use the HLT instruction. For more on core C states, see the Intel Core M Datasheet Volume 1.
- Intel® Transactional Sychronization Extensions - New Instructions (Intel® TSX-NI) provides the ability to fine grain lock while only programming coarse grain locks. See Intel® Architecture Instruction Set Extensions Programming Reference.
- A new Intel® AVX2 instruction, Floating Point fused Multiply Add (FMA), will help with face detection and other intensive compute applications.
- Be sure to optimize apps for touch. See the Ultrabook™ Device and Tablet Windows Touch Developer Guide, Developing with Desktop Natural User Interface APIs for Developers, and Handling touch input in Windows* 8 Applications.
- Optimize apps for sensor input including GPS, Compass, Gyroscope, Accelerometer, and Ambient Light. By using Intel® RealSense™ technology and Windows sensor APIs for 8.1 (see Ultrabook™ and Tablet Windows* 8 Sensors Development Guide and Detecting Ultrabook™ sensors on Windows* 8 ).
Other relevant Intel documentation and tools:
- Intel® RealSense™ 2014 SDK
- Intel® Graphics Developers Guide
- Intel® Media SDK
- Intel® Graphics Performance Analyzers (Intel® GPA)
- Intel® Advanced Vector Extensions (Intel® AVX)
- Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer Manuals
- List of Intel Software Developer Tools
- More information on the Intel Core M Processors
About the Author
Colleen Culbertson is a Platform Application Engineer with the Developer Relations Division, who authors articles and a regular blog on the Intel® Developer Zone.
Performance tests and ratings are measured using specific computer systems and/or components and reflect the approximate performance of Intel products as measured by those tests. Any difference in system hardware or software design or configuration may affect actual performance. Buyers should consult other sources of information to evaluate the performance of systems or components they are considering purchasing. For more information on performance tests and on the performance of Intel products, visit Intel Performance Benchmark Limitations.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Intel® Developer Zone offers tools and how-to information for cross-platform app development, platform and technology information, code samples, and peer expertise to help developers innovate and succeed. Join our communities for the Internet of Things, Android*, Intel® RealSense™ Technology and Windows* to download tools, access dev kits, share ideas with like-minded developers, and participate in hackathons, contests, roadshows, and local events.

