Modal and Modeless Dialog Box in C#
2.51/5 (25 votes)
This article describes the basic idea about modal and modeless in C#.
Introduction
I am originally an NDIS and Visual C++ programmer. I developed many applications in Visual C++ which handled dialog boxes. Then I got my first assignment in .NET which works on both Modal and Modeless dialog boxes. So I dug through MSDN and wrote the applicaton.
This article describes the basic idea about modal and modeless in C#.
Background
The first and most obvious question is, what is the difference between the Modal and Modeless dialog box?
The difference between a modal and modeless dialog box is that, modal dialogs once invoked will not allow the users to access the parent window, whereas modeless dialogs will allow the user to work with the parent window.
A user cannot enter input in any other dialog or invoke a menu option except without explicitly closing the modal dialog within the application. But the user can leave the modeless dialog open and do anything after the modeless dialog is invoked.
Using the Code
.NET is a superb and advanced, developer-friendly technology. Developers can concentrate on business models and all technology-specific things .NET does for you.
Writing Modal and Modeless dialog box applications is simple as compared with VC++/MFC. .NET provides rich classes set for Windows applications which make life easier.
The Form class is a base class for form-based applications (SDI/MDI/Dialog based). It provides you all the basic infrastructure for Windows (e.g. windows message loop, MDI Container etc).
So there is not any special class for dialogs, SDI, MDI like CDialog, CFrameWnd in MFC. You have to write only following line to run your application that’s all.
Application.Run(new Form1());
//Form1 is derived which is derived from Form.
This line initializes your application and also starts a message loop.
Showing a dialogbox is more simple than just calling ShowDialog() for modal dialog and Show() for modeless dialog that’s all.
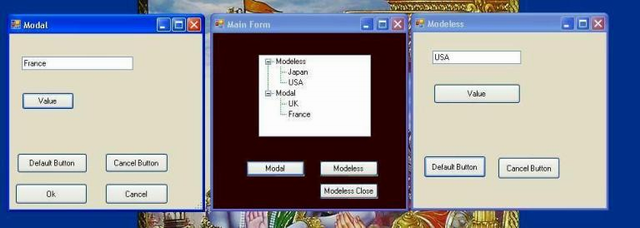
In my application, one main form and two dialog boxes. Main form creates a Modal dialog box and Modeless creates a dialog box when a user clicks on buttons.
There are two classes, Modal and Modeless for each dialog box. Both are derived from the Form class. Implementations of classes are the same.
class Modal : Form
{
//Implementation here
}
class Modeless : Form
{
//Implementation here
}
Next is displaying the dialog box:
Modeless dialog box can be displayed using following code:
Modeless objModeless = new Modeless();
objModeless.dlgevent += InfoEvent;
//Modeless dialog box is displayed by Show method.
objModeless.Show();
The Show() method is not blocking. It displays the dialog box and retuns.
The Modal dialog box can be displayed using the following code:
//Set event handler which is called by dialog box.
objModal.dlgevent += InfoEvent;
//ShowDialog dispalys dialog box.
//Return value in Modal constructor
if (DialogResult.OK == objModal.ShowDialog())
{
m_ModalTN.Nodes.Add("Ok Pressed");
}
ShowDialog() is a blocking method. It blocks until form is closed or the OK, Cancel button is not pressed.
Now let's discuss with Button handling in a dialog box.
Button is a standard class. It provides having many methods and properties. I will discuss a few important properties here.
DialogResult: This is one of the important properties. This value is returned by theShowDialogmethod when a user clicks on this button.It returns
DialogResult.DialogResultis assigned to a button which will work as OK and Cancel buttons.this.button2.DialogResult = DialogResult.OK; this.button3.DialogResult = DialogResult.Cancel;
button2andbutton3buttons will work as OK and Cancel buttons.DialogResult.OKandDialogResult.Cancelare assigned tobutton2andbutton3in my code.Text: This property can change your button name.
The Form class provides two important properties which are useful for dialog based application.
AcceptButton: This property makes default button for your formWhenever the user presses the ENTER key on the form then this property is hit.
CancelButton: This property makes the Cancel button for your form.Whenever a user presses the ESC key on the form then this method is hit.
Code snippet is below:
public Modal()
{
InitializeComponent();
//These values are returned from ShowDialog method.
this.button2.DialogResult = DialogResult.OK;
this.button3.DialogResult = DialogResult.Cancel;
//Following code makes default button and cancel button.
AcceptButton = DefaultButton;
CancelButton = Cancel;
}
I record all the dialog box actions in a treeview. I create the treeview on the main form.
The infoevent event is called whenever any action occurs on any of either dialog boxes.
This method also makes a bridge between the main form and other dialog boxes.
I created two tree’s head nodes Modeless and Modal.
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
///Add two top nodes in tree
m_ModelessTN = treeView1.Nodes.Add("Modeless");
m_ModalTN = treeView1.Nodes.Add("Modal");
}
This method changes the main form background color. BackColor is the form properties that changes a form’s background color. This method finds an object type at runtime and adds the value in the corresponding node.
Corresponding Node
private void InfoEvent(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Modeless objSrc = sender as Modeless;
//Set background color
this.BackColor = Color.FromArgb(new Random().Next(255), 0, 0);
if (null != objSrc)
{
m_ModelessTN.Nodes.Add(objSrc.TEXT);
}
else
{
Modal objModalSrc = sender as Modal;
if (null != objModalSrc)
{
m_ModalTN.Nodes.Add(objModalSrc.TEXT);
}
}
treeView1.ExpandAll();
}
And last but not least, how to close your application. It is very simple. Just call the Close form method. I also added a Modeless Close button.
The following code is the handler of this button.
private void ModelessClose(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
objModeless.Close();
}
Points of Interest
This is my first post to Code Project. I am very happy. Code Project helps me lot, improving my capabilities.
