This article explains how to automate the installation and configuration of a Ruby web application on an Ubuntu 14.04 LTS server using Ansible.
Introduction
Nowadays, you can get your own dedicated server up and running in a seconds. Once you get it up, do you really spend several hours to configure it for your application needs? Do you really want to repeat the same steps with each new server? In this article, I will give you an idea of automated installation with Ansible, a simple IT Automation toolkit and Ubuntu 14.04 LTS server as box OS.
Background
You would need basic understanding of ansible files syntax. if you did not play with Ansible yet, I would recommend to review some intro articles like http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/intro.html or perhaps one of the slideshares like this one?
Cooking
We would need to deploy the following components: Ruby, Web server with Passenger, your application itself. For purposes of the demo, we will install well known starter Devise
Ruby Switcher Chruby
I used to choose RMV previously, but recently, I am a fan of chruby - it is lightweight, quick to understand and just works - available at Github.
Upon studying installation instructions, we automate manual installation steps with Ansible, and get a bonus: reusable recipe to install the ch_ruby.
---
- name: Ruby | Check if chruby is present
shell: test -x /usr/local/bin/chruby-exec
when: ansible_system == "Linux"
ignore_errors: yes
register: chruby_present
tags: ruby
- name: Ruby | Download chruby distribution
get_url: url="http://github.com/postmodern/chruby/archive/v{{ chruby_version }}.tar.gz"
dest="/tmp/chruby-{{ chruby_version }}.tar.gz"
when: chruby_present|failed
tags: ruby
- name: Ruby | unpack chruby
command: tar xf "/tmp/chruby-{{ chruby_version }}.tar.gz"
chdir="/tmp"
when: chruby_present|failed
tags: ruby
- name: Ruby | chruby install target
command: make install
chdir="/tmp/chruby-{{ chruby_version }}"
become: yes
when: chruby_present|failed
tags: ruby
- name: Ruby | autoload script
template: src="{{role_dir}}/templates/ch_ruby.sh.j2" dest=/etc/profile.d/chruby.sh
become: yes
tags: ruby
Ruby install
Ruby-install is the second toolkit from the same author. At the present moment, this approach is the #1 choice for me when I need to install specific Ruby version. Tool is available at Github.
Once we study ruby-install setup notes, we can automate these steps with a series of ansible steps:
---
- name: Ruby | Check if ruby install is present
shell: test -x /usr/local/bin/ruby-install
when: ansible_system == "Linux"
ignore_errors: yes
register: rubyinstall_present
tags: ruby
- name: Ruby | Ruby install | package dependencies
apt: pkg={{ item }} state=present force="yes" update_cache="yes"
when: ansible_system == "Linux"
with_items:
- build-essential
- libffi-dev
- libgdbm-dev
- libncurses5-dev
- libreadline-dev
- libreadline6-dev
- libtinfo-dev
- libyaml-dev
become: yes
tags: ruby
- name: Ruby | Download rubyinstall
get_url: url=http://github.com/postmodern/ruby-install/archive/v{{ ruby_install_version }}.tar.gz
dest=/tmp/ruby-install-{{ ruby_install_version }}.tar.gz
when: rubyinstall_present | failed
tags: ruby
- name: Ruby | Unpack ruby-install
command: tar xf /tmp/ruby-install-{{ ruby_install_version }}.tar.gz
chdir=/tmp
when: rubyinstall_present | failed
tags: ruby
- name: Ruby | Run ruby-install install target
command: make install
chdir=/tmp/ruby-install-{{ ruby_install_version }}
when: rubyinstall_present | failed
become: yes
tags: ruby
- name: Ruby | Download list of rubies available
command: ruby-install
when: rubyinstall_present | failed
become: yes
tags: ruby
Ruby
Now it is time to install Ruby. Small comment here: if you deploy saying on shared server, you most likely would like to have an ability to have multiple ruby versions and switch between them. On the other hand, if you deploy your application to the dedicated host - usually I also replace default system ruby with the same ruby version.
With tools above, Ruby installation recipe is compact & clear:
---
- name: Ruby | Find out if ruby_version is already installed
stat: path={{rubies_location}}/ruby-{{ruby_version}}
register: ruby_version_present
tags: ruby
- name: Ruby | Install ruby_version if necessary
command: '/usr/local/bin/ruby-install ruby {{ruby_version}}'
when: not ruby_version_present.stat.exists
become: yes
tags: ruby
- debug: var="ruby_install_setsystem"
- name: Ruby | Update SYSTEM ruby_version if necessary
command: '/usr/local/bin/ruby-install --system ruby {{ruby_version}}'
when: option_ruby_install_setsystem
become: yes
tags: ruby
Webserver & Passenger
Thanks to Phusion Passenger team, they did a great job to provide pre-built binaries for most of the popular platforms and configurations at this link. This allows us to skip steps of compiling phusion passengers from source, recomplining webserver, etc. & use pre-built binary instead.
Historically, I prefer Nginx over classic Apache, thus we will install pre-build Nginx with passenger:
---
- name: Nginx | Check if is present
command: test -x /usr/sbin/nginx
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian"
ignore_errors: yes
register: nginx_present
tags: nginx
- name: Passenger | Add GPG key to apt keyring
apt_key: keyserver=keyserver.ubuntu.com id=561F9B9CAC40B2F7
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian" and nginx_present|failed
tags: passenger
become: yes
- name: Passenger | Install needed packages
apt: state=present pkg="{{item}}"
with_items:
- apt-transport-https
- ca-certificates
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian" and nginx_present|failed
become: yes
tags: passenger
- name: Passenger | Add nginx extras repository
apt_repository: repo="deb https://oss-binaries.phusionpassenger.com/apt/passenger trusty main" state=present
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian" and nginx_present|failed
tags: passenger
become: yes
- name: Ruby | Install Nginx extra and Phusion Passenger
apt: state=present update_cache=yes pkg="{{item}}"
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian" and nginx_present|failed
with_items:
- nginx-extras
- passenger
become: yes
tags: passenger
- name: Nginx | Create sites available/enabled directories
file: path={{item}} state=directory mode=0755
with_items:
- /etc/nginx/sites-available
- /etc/nginx/sites-enabled
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian" and nginx_present|failed
tags:
- nginx
- passenger
become: yes
- name: Nginx | Configure include sites-enabled
lineinfile: dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf regexp=".*sites-enabled.*"
line=" include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;" insertbefore="}" state=present
tags:
- nginx
- passenger
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian" and nginx_present|failed
become: yes
- name: Nginx | Disable default site
file: path=/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default state=absent
tags:
- nginx
- passenger
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian" and nginx_present|failed
become: yes
- name: Nginx | Uncomment server_names_hash_bucket_size
lineinfile: dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
regexp="^(\s*)#\s*server_names_hash_bucket_size"
line="\1server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;" backrefs=yes
become: yes
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian" and nginx_present|failed
tags:
- nginx
- passenger
- name: Nginx | Set ruby to system one
lineinfile: dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf regexp="^(\s*)#\s*passenger_ruby"
line="passenger_ruby /usr/local/bin/ruby;" backrefs=yes
become: yes
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian" and nginx_present|failed
tags:
- nginx
- passenger
- name: Nginx | Set ruby to system one
lineinfile: dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf regexp="^(\s*)#\s*passenger_root"
line="passenger_root /usr/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/phusion_passenger/locations.ini;"
backrefs=yes
become: yes
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian" and nginx_present|failed
tags:
- nginx
- passenger
- name: Nginx | Reload
service: name=nginx state=reloaded
when: ansible_os_family == "Debian" and nginx_present|failed
tags:
- nginx
- passenger
become: yes
Several comments to installation script above, which might require changes in your own scenarios:
- Task named "Create sites available/enabled directories" & the next one - it actually implements Apache like "sites-available / sites-enabled" folder structure for VHosts configs. If you prefer default setup - comment this out.
- Specifying ruby location to passenger with:
lineinfile: dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf regexp="^(\s*)#\s*passenger_ruby"
line="passenger_ruby /usr/local/bin/ruby;" backrefs=yes
As you see, replacement above assumes that system ruby is used. You might want to specify different Ruby path here.
Goal of these two tasks is to take nginx.conf & set two parameters: passenger_root and passenger_ruby as per original instuctions in the above comment.
##
# Uncomment it if you installed passenger or passenger-enterprise
##
passenger_root /usr/lib/ruby/vendor_ruby/phusion_passenger/locations.ini;
passenger_ruby /usr/local/bin/ruby;
How to validate that you've installed nginx with passenger right?
Execute these commands and validate the setup:
sudo /usr/bin/passenger-config validate-install
What would you like to validate?
Use <space> to select.
If the menu doesn't display correctly, press '!'
‣ ⬢ Passenger itself
⬡ Apache
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Checking whether this Passenger install is in PATH... ✓
* Checking whether there are no other Passenger installations... ✓
Everything looks good. :-)
and /usr/sbin/passenger-memory-stats - you should see both - Nginx & passenger processes.
sudo /usr/sbin/passenger-memory-stats
Version: 5.0.26
Date : 2016-03-18 11:17:57 +0200
------------- Apache processes -------------
*** WARNING: The Apache executable cannot be found.
Please set the APXS2 environment variable to your 'apxs2' executable's filename,
or set the HTTPD environment variable to your 'httpd' or 'apache2' executable's filename.
--------- Nginx processes ----------
PID PPID VMSize Private Name
------------------------------------
8768 9991 138.1 MB 1.1 MB nginx: worker process
8769 9991 137.8 MB 0.9 MB nginx: worker process
8770 9991 137.8 MB 0.9 MB nginx: worker process
8771 9991 137.8 MB 0.9 MB nginx: worker process
9991 1 137.8 MB 0.9 MB nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx
### Processes: 5
### Total private dirty RSS: 4.68 MB
---- Passenger processes -----
PID VMSize Private Name
------------------------------
8742 436.3 MB 1.0 MB Passenger watchdog
8745 982.9 MB 2.0 MB Passenger core
8756 444.5 MB 1.1 MB Passenger ust-router
8806 387.1 MB 69.3 MB Passenger RubyApp: /var/www/public (production)
### Processes: 4
### Total private dirty RSS: 73.47 MB
slavko@ERM:/etc/nginx$
Application Setup Itself
Let's define application parameters: in particular: required OS packages to build gems, app secret - to hash the passwords, application environment parameters, database connection details.
app_dependencies:
- libsqlite3-dev
- libmysqlclient-dev
- libpq-dev
- git
- nodejs
- npm
app_short_name: app
app_env: production
app_domain: domain.local
app_secret: 82d58d3dfb91238b495a311eb8539edf5064784f1d58994679db8363ec241c745bef0b446bfe44d66cbf91a2f4e497d8f6b1ef1656e3f405b0d263a9617ac75e
app_repository: https://github.com/RailsApps/rails-devise.git
# app_repository_keyname: id_rsa_app
app_base_dir: /var/www
app_www_root: "{{app_base_dir}}/public"
app_env_vars:
- {name: SECRET_KEY_BASE, value: "{{app_secret}}" }
- {name: DATABASE_URL, value: "postgres://{{app_db_user}}:
{{app_db_password}}@{{app_db_host}}/{{app_db_name}}"}
- {name: RAILS_ENV, value: "{{app_env}}" }
- {name: DOMAIN_NAME, value: "{{app_domain}}" }
app_db_host: localhost
app_db_user: app_user
app_db_password: app_password
app_db_name: app_database
app_directories:
- "{{app_base_dir}}"
And application provisioning script itself, which goes into stages: OS packages dependencies, Gem dependencies (for devise, it is sqlite3), checking out the source code, patching Gem file so the ruby version matches the one installed on host + introducing production gems for uglifyjs (this is current app specifics), bundle install, patching database configuration, assets compilation, db migration, generating nginx site configuration, restarting the web server.
---
- name: APP STUB | Dependencies
apt: pkg={{ item }} state=present force="yes" update_cache="yes"
when: ansible_system == "Linux"
with_items: "{{app_dependencies}}"
become: yes
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | Install gem dependencies
shell: "gem install --no-rdoc --no-ri {{item}}"
with_items:
- sqlite3
become: yes
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | Re-create base app directory
file: path={{app_base_dir}} state=absent
become: yes
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | Create directories
file: path={{item}} state=directory mode=0755
owner={{ansible_user_id}} group={{ansible_user_id}}
with_items: "{{app_directories}}"
become: yes
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | Checkout app without key
git: repo="{{app_repository}}" dest="{{app_base_dir}}"
accept_hostkey="yes" force="yes"
when: app_repository_keyname is not defined
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | Install global rails gem
shell: gem install --no-rdoc --no-ri rails
become: yes
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | Eliminate ruby req
lineinfile: dest="{{app_base_dir}}/Gemfile" regexp="^(\s*)*ruby"
line="ruby '{{ruby_version}}'"
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | gem therubyracer - uglifyjs
lineinfile: dest="{{app_base_dir}}/Gemfile" regexp="^(\s*)*gem 'therubyracer'"
line="gem 'therubyracer', :platforms => :ruby" insertafter="^group :production do"
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | gem execjs - uglifyjs
lineinfile: dest="{{app_base_dir}}/Gemfile" regexp="^(\s*)*gem 'execjs'"
line="gem 'execjs'" insertafter="^group :production do"
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | gem pg
lineinfile: dest="{{app_base_dir}}/Gemfile" regexp="^(\s*)*gem 'pg'"
line="gem 'pg'" insertafter="^group :production do"
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | Run bundle install --path .bundle/gems --binstubs .bundle/bin
shell: bundle install --path .bundle/gems --binstubs .bundle/bin
args:
chdir: "{{app_base_dir}}"
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | database.yml
template: src="{{root_dir}}/templates/app/database.yml.j2"
dest="{{app_base_dir}}/config/database.yml"
become: yes
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | Precompile assets
shell: bundle exec rake assets:precompile
args:
chdir: "{{app_base_dir}}"
environment:
RAILS_ENV: "{{app_env}}"
DATABASE_URL: "postgres://{{app_db_user}}:{{app_db_password}}@{{app_db_host}}/{{app_db_name}}"
SECRET_KEY_BASE: "{{app_secret}}"
DOMAIN_NAME: "{{app_domain}}"
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | DB Migrate
shell: bundle exec rake db:migrate
args:
chdir: "{{app_base_dir}}"
environment:
RAILS_ENV: "{{app_env}}"
DATABASE_URL: "postgres://{{app_db_user}}:{{app_db_password}}@{{app_db_host}}/{{app_db_name}}"
SECRET_KEY_BASE: "{{app_secret}}"
DOMAIN_NAME: "{{app_domain}}"
tags: app_stub
- name: APP STUB | Nginx conf
template: src="{{root_dir}}/templates/nginx_app.conf.j2" dest="/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/{{app_short_name}}.conf"
become: yes
tags: app_stub
- name: Nginx | Reload
service: name=nginx state=reloaded
become: yes
tags: app_stub
In particular, we patch database config/database.yml with real connection details:
# On Heroku and other platform providers, you may have a full connection URL
# available as an environment variable. For example:
#
# DATABASE_URL="postgres://myuser:mypass@localhost/somedatabase"
#
# You can use this database configuration with:
#
production:
url: <%= ENV['DATABASE_URL'] %>
and we patch Nginx app site config to provide app environment variables to ruby app with passenger_env_var instructions.
server {
listen 80 default_server;
passenger_enabled on;
{% for envvar in app_env_vars %}
passenger_env_var {{ envvar.name }} "{{ envvar.value }}";
{% endfor %}
passenger_app_env {{app_env}};
root {{app_www_root}};
}
Running the Code
Let's execute provisioning and test it, for purposes of the demo - we will use local postgres as a DB.
---
- hosts: www
vars:
- root_dir: ..
roles:
- {
role: "sa-postgres",
option_create_app_user: true
}
- {
role: "sa-ruby",
ruby_install_setsystem: true,
ruby_version: 2.3.0,
option_install_sampleapp: true,
option_install_nginx_passenger: true
}
Once application provisioning process is over:
TASK: [sa-ruby | Nginx | Reload] **********************************************
changed: [192.168.0.17] => {"changed": true, "name": "nginx", "state": "started"}
PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************
192.168.0.17 : ok=55 changed=46 unreachable=0 failed=0
Play run took 23 minutes
So, depending on network speed, you have your application installed.
Let's check by IP address:
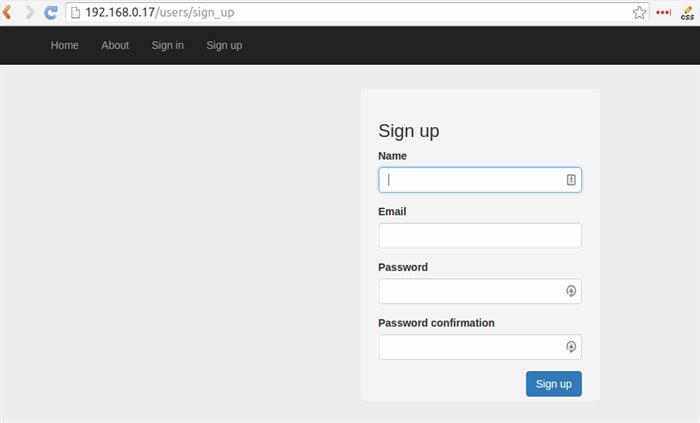
Points of Interest
Now you are aware of another way to deploy your Ruby applications.
Demo deployment script is available here, recipes packed as Ansible reusable role available here.




